Mobile phone connectors are crucial electronic components in modern smartphones. They act like the phone’s “neural network,” connecting various functional modules and ensuring stable transmission of electrical signals and power.
The quality of these seemingly small components directly affects the overall performance and reliability of the phone. Statistics show that the vast majority of after-sales quality problems with mobile phones are related to connectors, demonstrating their critical role in mobile phone design.

FPC Connectors: The “Flexible Nerves” of the Device
FPC connectors are used to connect LCD displays, camera modules, etc., to the main circuit board. Their biggest feature is the use of flexible materials, allowing them to be bent and folded, perfectly adapting to the compact and irregular spatial layout inside the phone. For example, in the hinge area of a foldable phone, the FPC connector uses a special “wavy” wiring layout to release stress, ensuring conductivity stability during dynamic bending.
Currently, the mainstream pin pitch of FPC connectors is 0.4mm, and it is developing towards 0.3mm and even smaller pitches. Some advanced products even achieve a pitch of 0.2mm, with a contact width of only 0.1mm, equivalent to the diameter of a human hair.
This miniaturization technology makes it possible to further narrow the bezels of mobile phone screens. In the future, with the popularization of new flexible substrates such as LCP, the high-frequency signal transmission performance of FPC connectors will be further improved to meet the needs of 5G millimeter-wave communication.
Board-to-Board Connectors: The “Skeleton” of Modular Design
Board-to-board connectors are key components for connecting different circuit boards inside a mobile phone, such as connecting the motherboard and sub-boards, or the motherboard and camera module. They use a male-female connector design, achieving circuit conduction through the tight contact of metal terminals.
Modern smartphones pursue modular design for easy maintenance and functional upgrades, and board-to-board connectors play a core role in this process. Their technological development focuses on “small pitch and low height,” with the current mainstream pitch at 0.4mm, gradually moving towards 0.35mm and even smaller pitches, and the height reduced to 0.9mm or even lower. Meanwhile, to combat high-frequency signal interference, shielding has become a standard feature of high-end board-to-board connectors.
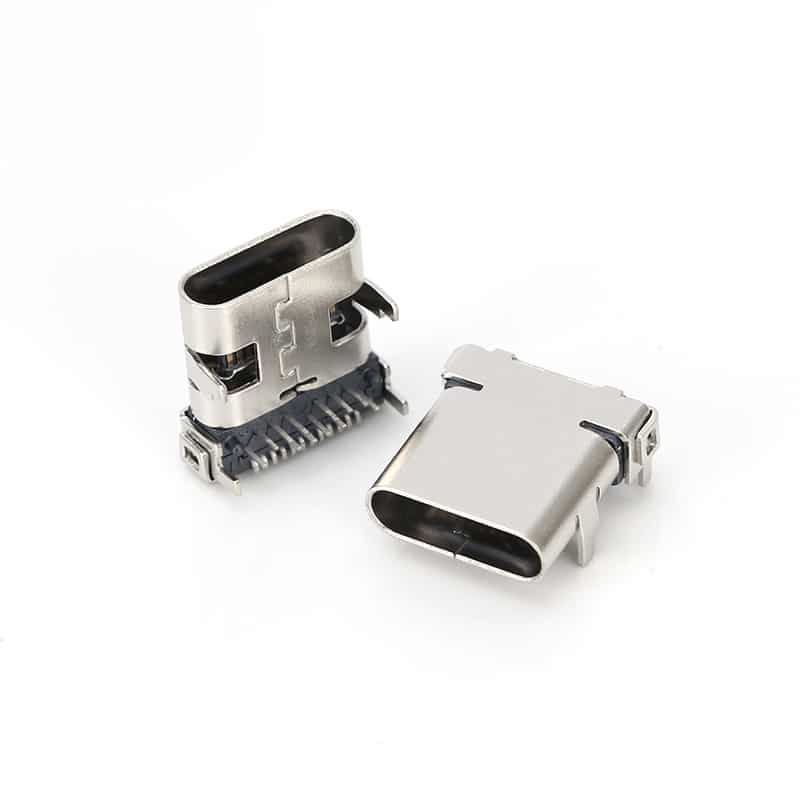
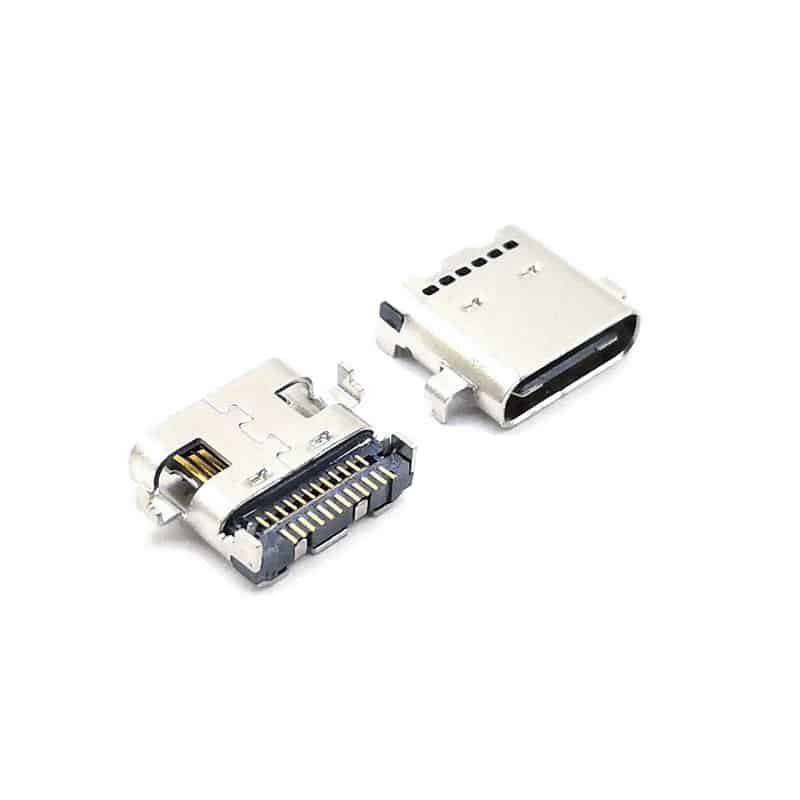
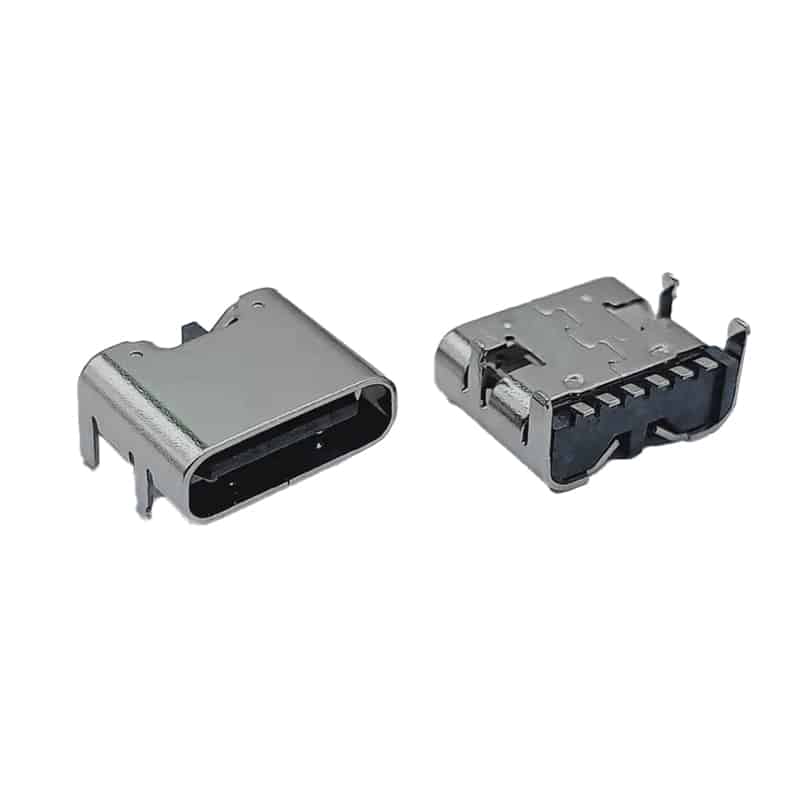
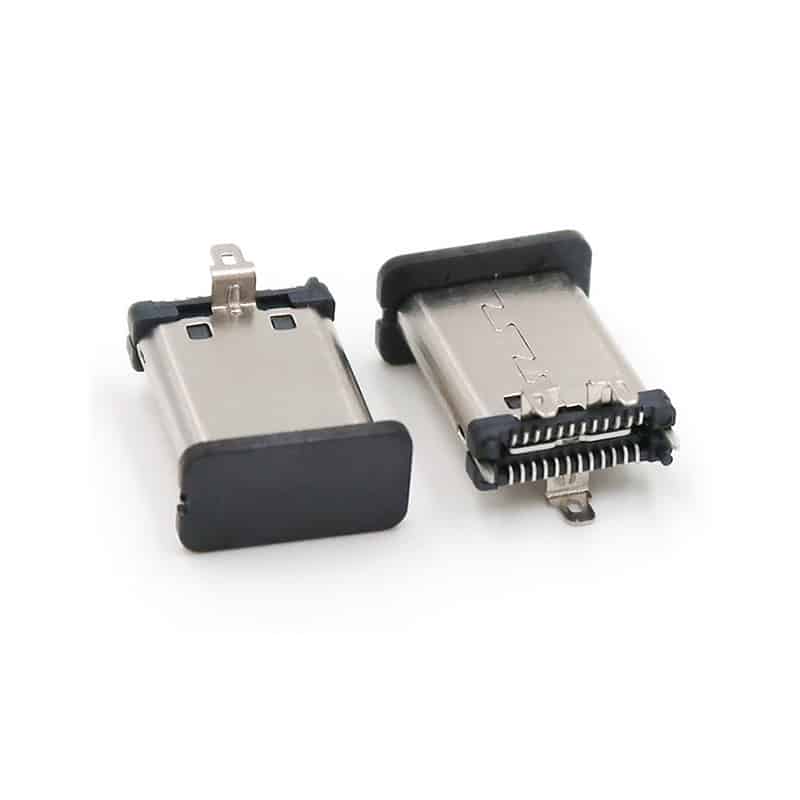
I/O Connectors: The External “Data Bridge”
I/O connectors serve as the channel for data and power transmission between mobile phones and external devices, handling charging and data synchronization. From early Mini USB and Micro USB to the now dominant Type-C, the history of I/O connector development is also a history of the standardization evolution of mobile device interfaces.
Type-C interfaces have rapidly gained market acceptance due to their advantages such as reversible insertion, high-speed data transmission (e.g., USB 3.2 Gen 2), and high-power charging (e.g., USB PD 3.0). In the future, while continuing the standardization trend, I/O connectors are developing towards thinner designs, waterproofing (e.g., IP68 rating), and higher integration (e.g., integrated audio functions).

Battery Connectors: The Device’s “Power Lifeline”
Battery connectors are responsible for the stable power connection between the phone’s motherboard and the battery. Depending on their structure, they are mainly divided into two types: spring-loaded and blade-type. Spring-loaded connectors rely on the elastic pressure of a spring to maintain contact, while knife-switch connectors use an insertion structure.
Because battery connectors transmit relatively large currents (typically several amperes), and mobile phones may face complex environments such as vibration and drops, low contact resistance and high connection reliability are crucial. Technological trends focus on miniaturization, new battery interface designs, and how to further reduce contact resistance to ensure charging safety and efficiency.
Card Connectors: The “Gateway” to Expanded Storage
Card connectors are primarily used to install and connect SIM cards (User Identity Modules) and external storage cards (such as T-flash cards, i.e., Micro SD cards). SIM card connectors are mainly 6-pin, and their development trend is towards ultra-low thickness (e.g., 0.50mm) and multi-functional integration.
Products that combine SIM card connectors and T-flash connectors into one unit have already appeared on the market. This integrated design helps save internal space in mobile phones. Meanwhile, with the promotion of eSIM technology, the use of traditional physical SIM card connectors may gradually decrease, but at present, it remains an essential component in mobile phones.
Antenna Connectors: The “Invisible Channel” for Signals
Antenna connectors connect the phone’s motherboard to the antenna, and their shape and design directly impact the antenna’s high-frequency performance. Improper design can lead to poor signal strength and instability.
In the 5G era, due to the higher frequencies and greater transmission losses of millimeter waves, even more stringent requirements are placed on antenna connector performance. They need to maintain low insertion loss (e.g., <0.5dB/mm) in high-frequency bands such as 38GHz to ensure the stability of high-speed 5G data transmission. Therefore, antenna connector design has become a key aspect of optimizing phone RF performance.
Camera Socket Connectors: The “Dedicated Channel” for Images

Camera socket connectors are specifically designed to connect camera modules. They not only provide electrical connections but also offer excellent electromagnetic shielding for sensitive camera signals through a metal shielding shell, preventing signal interference and ensuring image quality.
This type of connector facilitates the repair and replacement of camera modules, aligning with the trend of modular repair in mobile phones. Its development exhibits a coexistence of standardization and customization, with mobile phone manufacturers selecting the most suitable connector solution based on different camera configurations.
Summary of the mobile phone connector
Although small, mobile phone connectors are the cornerstone of the complex functions of smartphones. With the advancement of new technologies such as 5G, foldable screens, and metaverse, mobile phone connectors are continuously developing towards miniaturization (smaller pitch, lower height), high performance (higher frequency, faster speed), high reliability (more durable and stable), and environmental friendliness (halogen-free and lead-free materials).
In the future, we have reason to believe that mobile phone connector technology will continue to break through, providing more possibilities for innovative smartphone designs.
We hope this detailed introduction will help you gain a more comprehensive understanding of these crucial “bridges” in mobile phones.