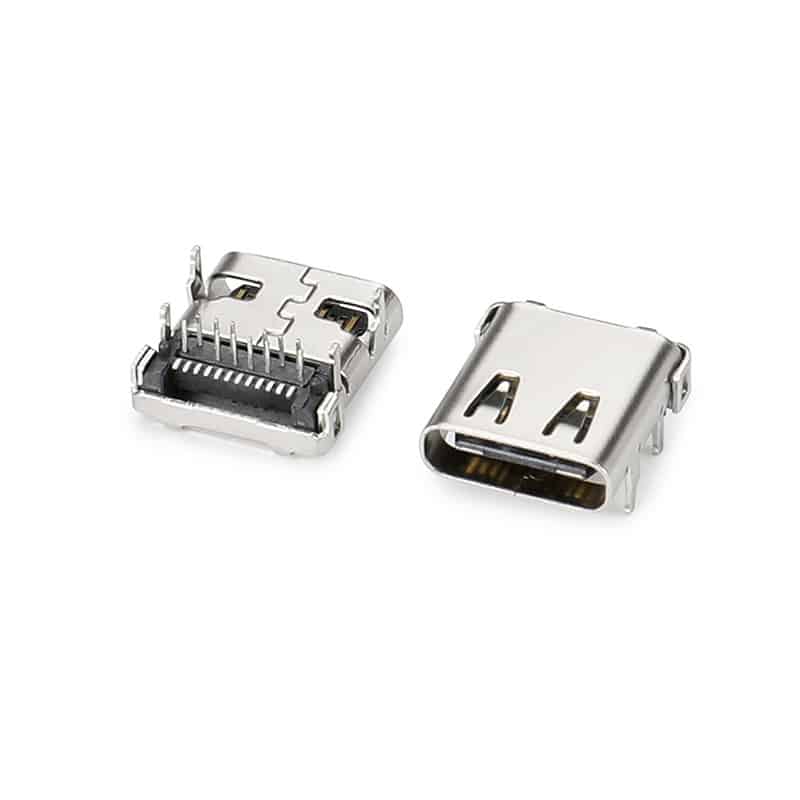
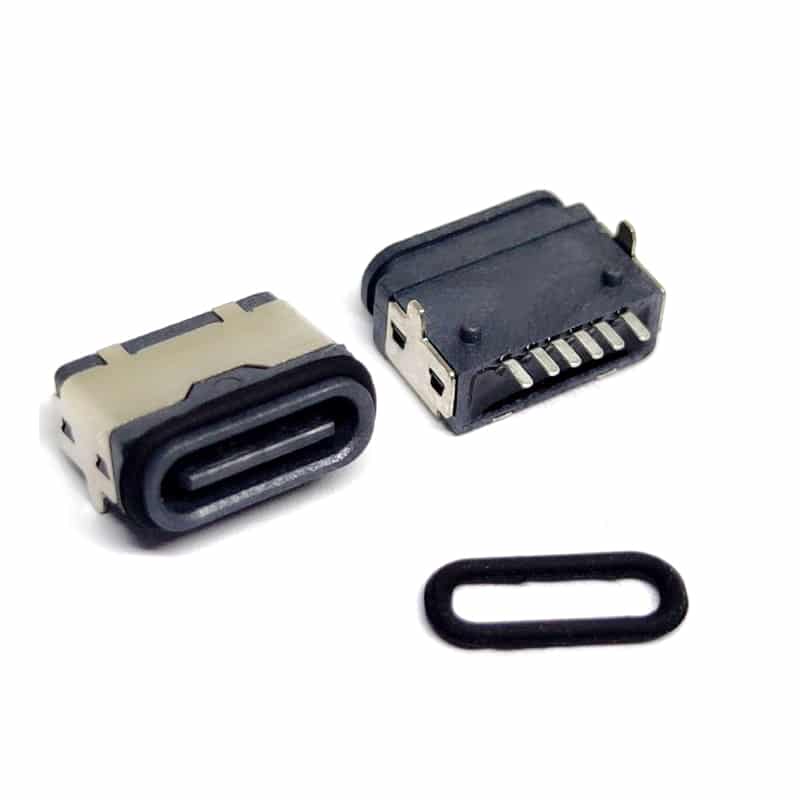
Choosing a USB-C connector with different pin configurations primarily involves a trade-off between functional completeness and cost to suit diverse application scenarios.
The table below provides a quick overview of their core differences in different pins.
| Pin Configuration | Core Functional Features | Typical Application Scenarios | Cost Considerations |
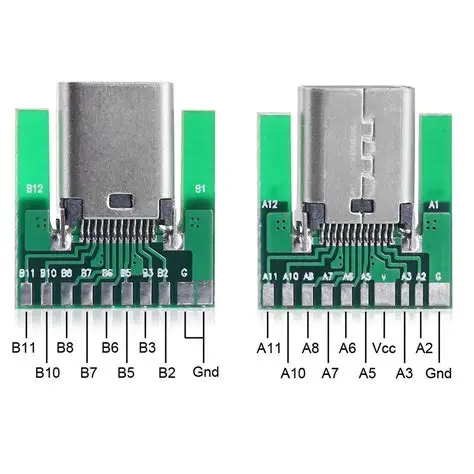
| 24-pin (Full-featured) | Supports all functions including high-speed data transfer (USB 3.0/3.1/4), PD fast charging, DisplayPort video output, and audio transmission. | High-end laptops (such as MacBooks with Thunderbolt interfaces), docking stations, high-performance motherboards, and devices requiring high-definition video transmission or high-speed file transfer. | Highest. Due to the inclusion of all pins and high-speed signal lines, the internal structure is complex, potentially requiring multi-layer PCBs and additional shielding layers, resulting in higher material and manufacturing costs. |
| 16-pin (USB 2.0 type) | High-speed data transfer functionality is removed (TX/RX differential pairs are removed), only supporting USB 2.0 speed (480Mbps), but retaining PD fast charging, USB 2.0 data transfer, and configuration channel (CC) functions. | Mice, keyboards, printers, small home appliances, and other ordinary digital peripherals that do not require high data transfer speeds. The main control MCUs of these devices often do not support USB 3.0 themselves. | Medium. Significantly reduces costs by simplifying high-speed signal pins, making it a mainstream cost-effective choice that balances cost and functionality. |
| 6-pin (Charging only) | Only retains VBUS (power), GND (ground), and CC1/CC2 (configuration channel) pins. Only supports charging, with no data transfer functionality. | Electric toys, electric toothbrushes, small fans, LED desk lamps, and other simple electrical appliances that only need to draw power via USB and do not require data communication. | Lowest. The simplest structure, with the fewest components and solder joints, offering significant cost advantages in mass production. |
The Root of Cost Differences
The number of pins directly determines the complexity and materials used in the connector, thus affecting the cost:
- 24-pin: As the full-featured version, its internal structure is the most complex. For example, high-specification cables (such as Apple’s Thunderbolt 4 Pro cable) may contain multiple layers of PCB boards, blind vias, and embedded vias internally, and utilize serpentine routing for precise impedance matching and length compensation to ensure high-speed signal integrity. These precise manufacturing processes and additional shielding layers and stress relief structures drive up costs.
- 16-pin vs. 6-pin: By removing high-speed data transmission pins or all data pins, the internal structure and cable design are significantly simplified. For example, inexpensive connectors may lack metal shielding, and the stress relief mechanism may be a simple rubber component instead of metal reinforcement. This design minimizes costs while fulfilling basic functions (charging or USB 2.0 data transmission).
Additional Considerations for Industrial Selection
Beyond consumer electronics, industrial, automotive, and outdoor equipment have vastly different requirements for USB-C connectors, and their cost structures vary accordingly:
Reinforced Structure and Locking Mechanism: Industrial-grade USB-C connectors use screw locking, snap locking, or push-pull self-locking mechanisms to prevent loosening in vibrating environments. The housing is usually all-metal or metal-clad, costing significantly more than consumer-grade plastic housings.
Ultra-High Protection Rating: Requires IP65/IP67 or even higher levels of dust and water resistance, demanding precise sealing rings (such as silicone rings) at the connector interface and extremely high requirements for the assembly process.
Wide Temperature Range and Durability: The operating temperature range may require -40°C to +105°C, and the terminal materials, plating, and plastics must withstand extreme temperature changes and a higher number of mating cycles (e.g., over 10,000 cycles).
Electromagnetic Compatibility: In industrial control or medical equipment, additional 360° full shielding and integrated ferrite rings may be required to suppress electromagnetic interference and ensure stable equipment operation.
Important Note: In these scenarios, the cost of the connector itself increases significantly, but compared to the system downtime, repairs, or safety risks caused by connector failure, this investment is necessary and highly cost-effective.
Selection Decision Flowchart: From Requirements to Model
After determining the basic pin configuration, further selection is still needed. You can complete the final selection decision based on the following path:
When choosing a USB-C connector, you can follow this decision path:
- Do you need any form of data communication (even at USB 2.0 speed)?
- Yes -> Choose a 24-pin full-featured type.
- No -> Proceed to the next step.
- Clarify your needs: Does your device require high-speed data transmission (>5Gbps) or video output?
- Yes -> Choose a 16-pin USB 2.0 type, which is the most economical data solution.
- No, the device only needs charging -> Choose a 6-pin charging-only type.
Practical Advice:
Sample Testing is Crucial: Before mass purchasing, be sure to request samples from the supplier and conduct insertion force tests, swing tests, salt spray tests (if applicable), and actual data and charging performance tests.
Focus on the Supply Chain: For consumer products, ensure that the selected model has multiple qualified suppliers to mitigate supply risks.
Certification and Compliance: Ensure that the connector (especially those used for high-voltage fast charging) passes relevant USB-IF certification and safety standards (such as UL/IEC). Using uncertified connectors may lead to compatibility issues and safety hazards.
Forward-Looking Trends: More Than Just Pin Count
The value differentiation of future USB-C connectors will extend beyond just the number of pins:
Integration and Miniaturization: Integrating passive components such as ESD protection diodes and common-mode chokes into the connector module to save PCB space is the direction of high-end design.
Thermal Design: With the PD 3.1 protocol supporting up to 240W (48V/5A) power, thermal design of high-power USB-C connectors and ports (such as using high thermal conductivity materials) will become a new cost and technical consideration.
Convergence of Professional and Consumer Markets: With the popularization of USB4/Thunderbolt 4 in the consumer market, many full-featured 24-pin connector designs (such as enhanced shielding) originally belonging to the professional field are gradually being adopted in high-end consumer products.

Selection Summary
In short, choosing a USB-C connector is an art of finding the best balance between “function, cost, and reliability.” A clear product definition is the starting point, while a deep understanding of application scenarios and meticulous control of the supply chain are key to ensuring the success of the final product.
Hopefully, this detailed comparison will help you make the most suitable USB-C connector selection decision based on your specific product positioning and budget. If you can share the specific type of target product, I may be able to provide a more targeted analysis.








