USB Type C Pinout Guide and Features:
USB-C, or USB Type-C connector, is a 24-pin connector (not a protocol) that replaces previous USB connectors and can carry audio, video, and other data.
24 Pin USB Type C Pinout
The 24 pin Type C Connectors has the most comprehensive functions, including the functional pin that supports PD fast charging, USB 3.0/USB 3.1, USB 2.0. Consequently, it can transmit audio, video and communication protocols and other data.
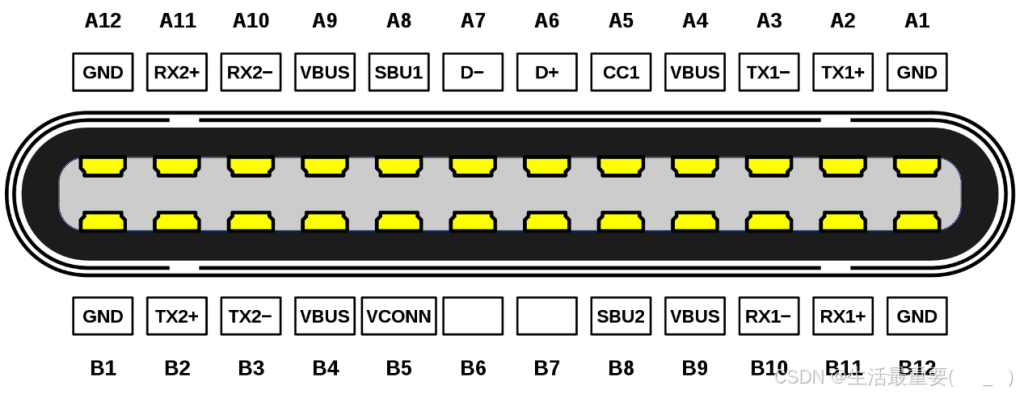
USB Type C Pinout diagram of the plug:
USB Type C Pinout diagram of receptacle:
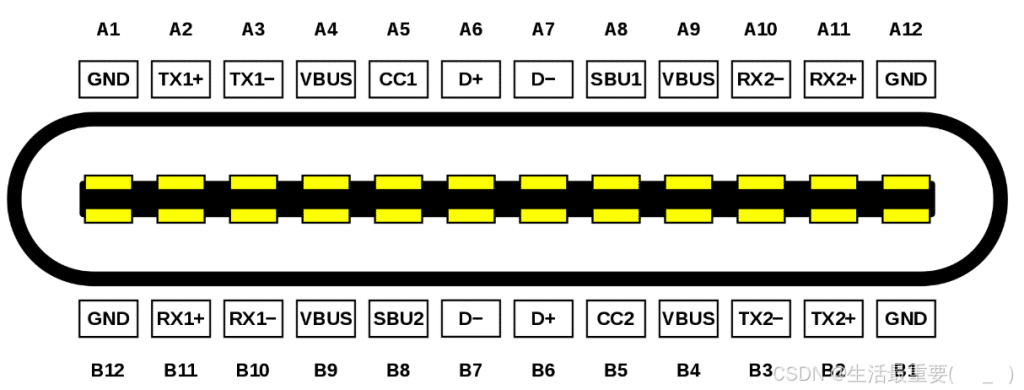
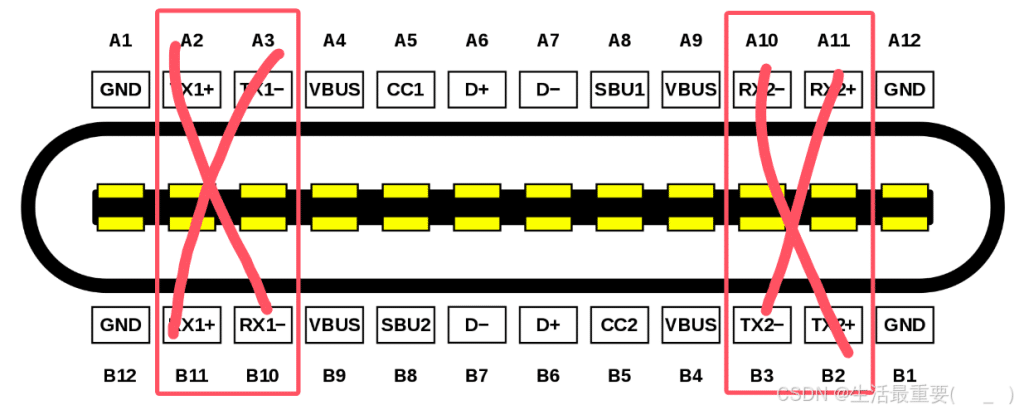
The upper and lower pins of the receptacle are not diagonally symmetrical but are instead symmetric about the central origin point. When a Type-C connector is inserted, it detects whether it is plugged in upright or reversed and then configures the pin assignments.
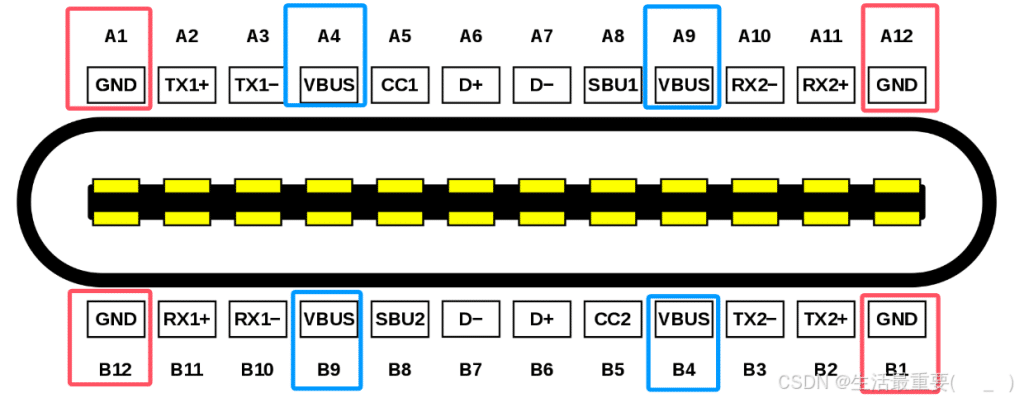
VBUS&GND
In the Type C interface, there are four sets of VBUS pinouts, mainly to offer higher contact current rating (up to 5A) rather than to provide higher voltage.
By default, VBUS offers 5V voltage, however, according to PD (Power Delivery) Protocol, voltage can be negotiated and increased up to 20V. It is the PD protocol that supplies higher voltage capability.
As a result, the Type C interface can support power delivery of up to 100W. This high-power output makes Type-C particularly suitable for fast charging and high-power device applications.
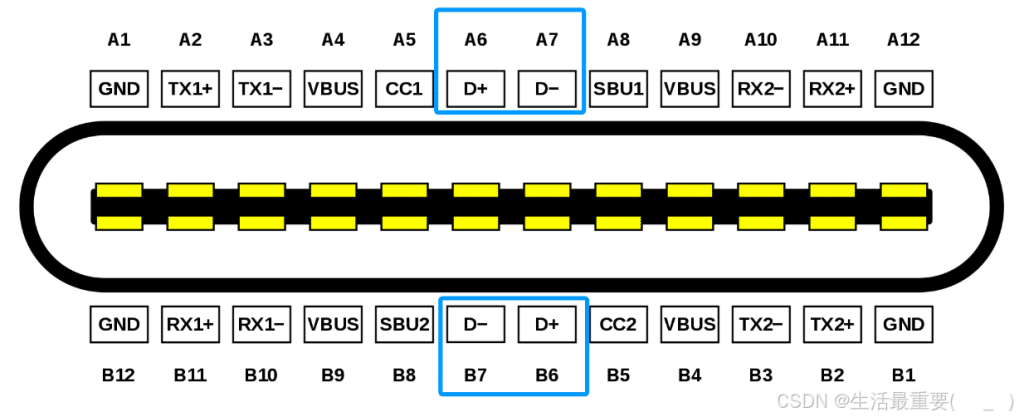
D+/D-
D+ and D- are the USB 2.0 data lines. The pins B6 and B7 in the Type C plug are left undefined, ensuring that only one set of USB 2.0 lines is connected between the receptacle and plug, regardless of insertion orientation.
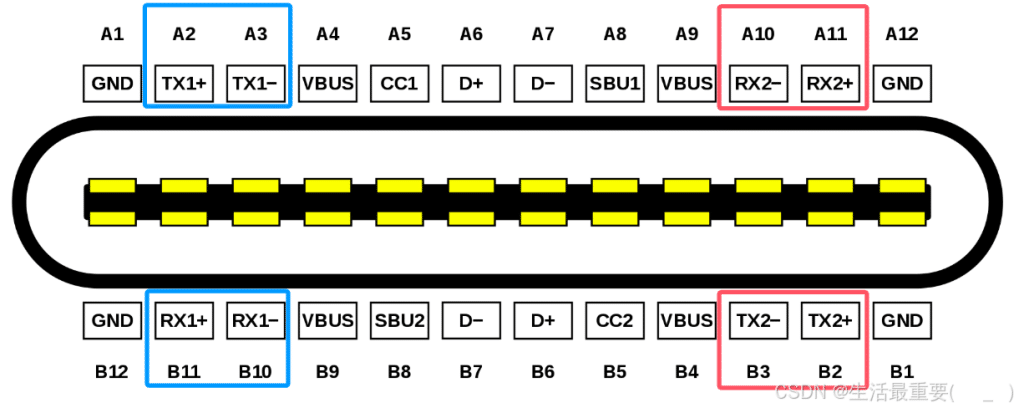
TX1+, TX1-, RX1+, RX1- , TX2+, TX2-, RX2+, RX2-
TX1+, TX1-, RX1+, RX1- and TX2+, TX2-, RX2+, RX2- are two sets of USB 3.0 data lines.
In reality, USB 3.0 data transmission only requires one set of differential pairs. However, the interface is designed with two sets – one is used for reversible insertion.
This means one set is always idle during operation. By upgrading the transmission protocol, the idle differential pairs can be utilized to double the efficiency of transmission. This enables the transmission of high-definition video data (DP signals), which is USB 3.1.
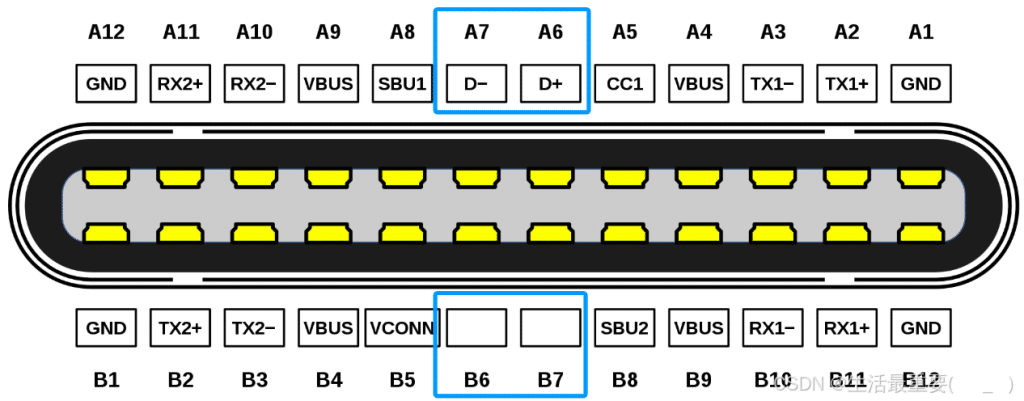
SBU1, SBU2
SBU1 and SBU2 serve as optional auxiliary channels that enable additional functionalities for Type-C interfaces. These functionalities may include audio/video signal transmission and device configuration data exchange.
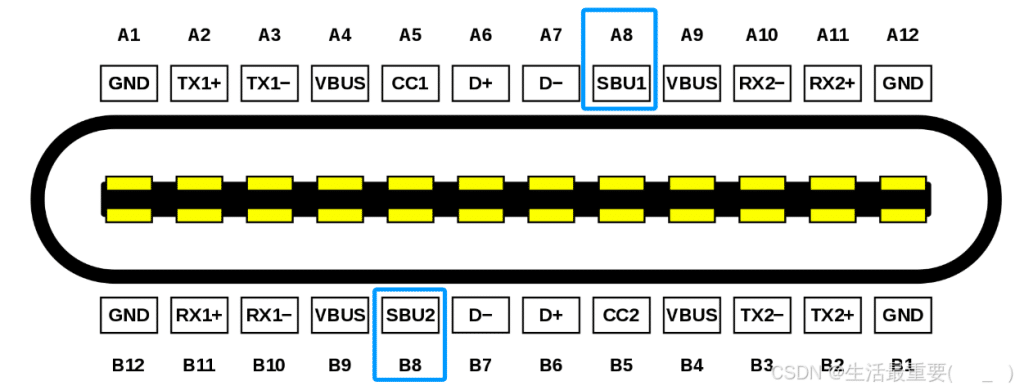
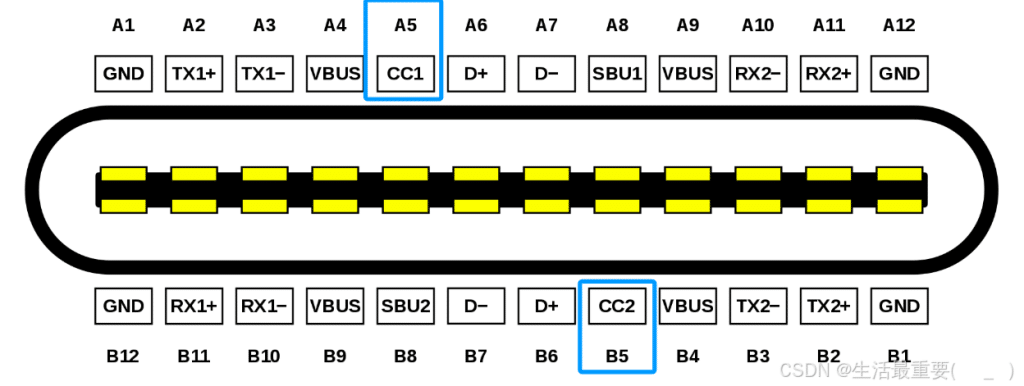
CC1, CC2
CC1 and CC2 pins are used to determine insertion orientation. When a Type-C plug is inserted into the receptacle, CC1 and CC2 pins are located on opposite sides of the connector. The host detects voltage or resistance changes on these pins to identify plug orientation:
-
- If CC1 detects voltage/resistance changes, it indicates that the plug is upright insertion.
- If CC2 detects changes, it indicates the plug is reverse insertion.
Furthermore, CC1 and CC2 pins play important roles in device connection detection, configuration data transmission, data direction comfirmation, power management and USB PD suppors.
16 Pin/12 Pin USB Type C Pinout
The 24 pin USB Type C Pinout to 16 pin eliminates the function of USB 3.1/USB 3.0. Therefore, there are not pins with corresponding function: TX1+/TX1-, RX1+/RX1-, TX2+/TX2-, and RX2+/RX2-.
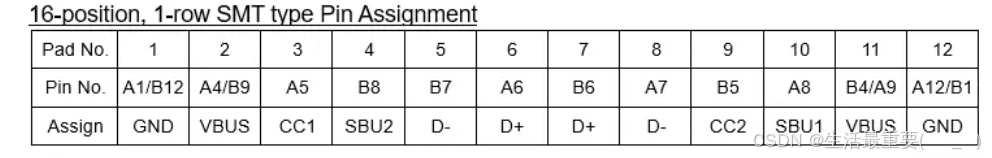
Actually, 12P and 16 pin is the same interface, the 12 pin Type C combines four VBUS pins into two pairs, and four GND pins into two pairs. While, actually the 16 pin Type C exposes 16 pins, and pad are only required 12 pins.
Both 16pin USB Type C Pinout and 12pin USB Type-C Pinout share identical physical packaging.
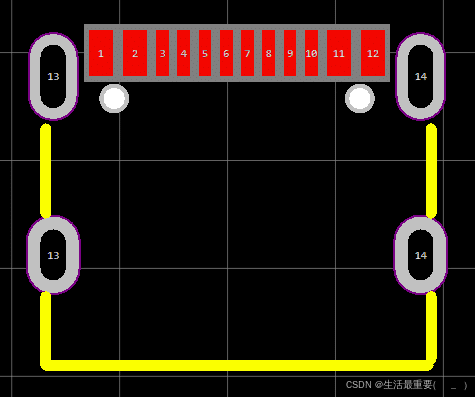
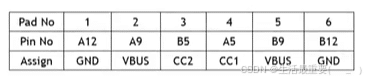
6 Pin USB Type C Pinout
The 6 pin Type C only remains VBUS and GND, CC1, CC2 pins. In this case, it can only achieve fast charging, CC1 and CC2 are used for transmition of device identication and fast charging protocol, and also supports power delivery up to100W.
Component Selection For USB-C Connectors
The 24 pin Type-C interface offers richer functions and higher performance, making it widely applicable in scenarios requiring high-speed data transfer and high current charging, such as smartphones, tablets, VR devices, and gaming consoles.
The 16 pin/12 pin Type C interface lacks USB 3.0/USB 3.1 function, making it suitable for small household appliances. Because their MCU do not support USB 3.0, USB 2.0 is sufficient. For example, mice, keyboards, and printers.
The 6-pin Type-C interface has no communication capability and is ideal for devices that only require USB charging, such as toys, electric toothbrushes, and small fans.
When designing a product, if communication is needed but the MCU have no USB 3.0 function, it can select 16P/12P.Selecting 24P would increase circuit costs and complicate soldering.
If the device is powered by a lithium battery and only requires USB charging, the 6-pin version can be selected to reduce circuit costs and simplify soldering.