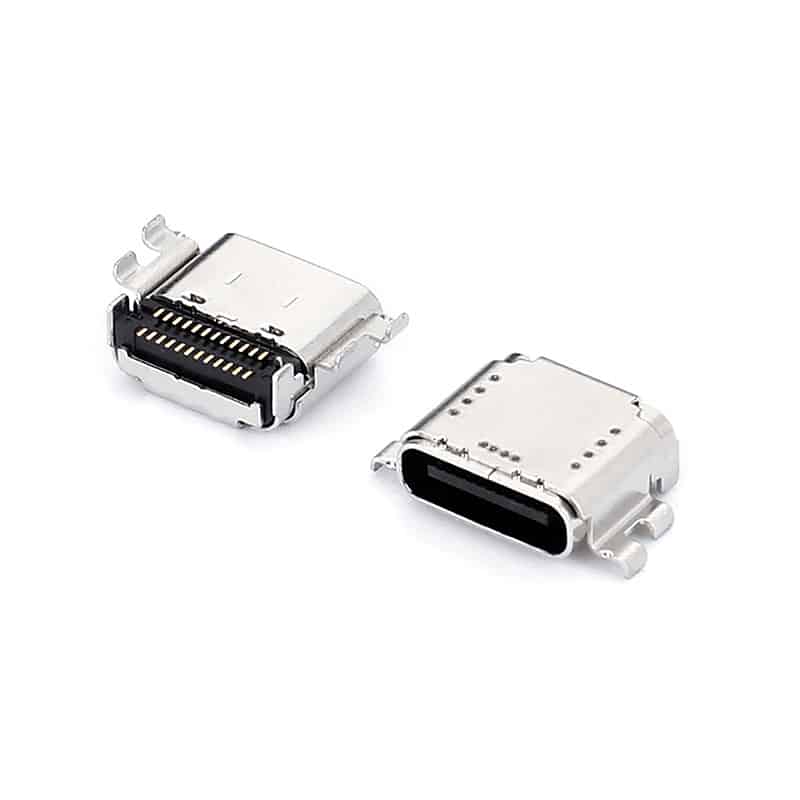
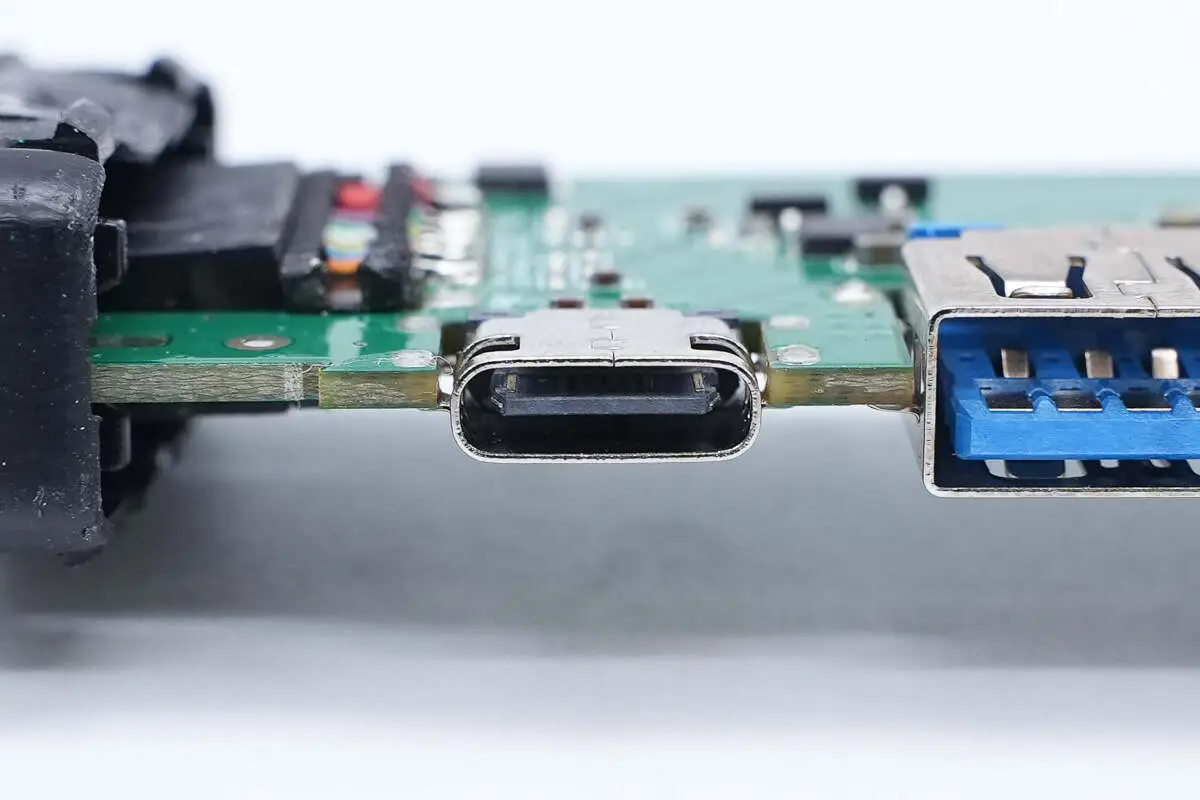
Des: USB3.1 type-c female connectors panel mount Type C connector USB 16 pin SMT on board
Part No: USB-TC16-F13
Specification:
Rating: 5A ,30VDC
Insertion force: 20N Max
Withdrawal force: 5-20N
Operating Life: 10,000Cycles
Packaging: Reel/Tray

Des: USB3.1 type-c female connectors panel mount Type C connector USB 16 pin SMT on board
Part No: USB-TC16-F13
Specification:
Rating: 5A ,30VDC
Insertion force: 20N Max
Withdrawal force: 5-20N
Operating Life: 10,000Cycles
Packaging: Reel/Tray
In industrial automation equipment, the protective standards that USB type C PCB connector must meet are significantly more stringent than those in the consumer electronics sector, primarily to address the challenges of harsh environments. The table below summarizes these critical protective standards and requirements for a quick overview. Protection Category Core Standard / Rating Significance and Requirements in Industrial Environments

The Type-C USB4.0 connector is a high-performance, universal connectivity standard based on the USB-C physical interface and the USB4 protocol, designed to unify the interface for data transmission, video output, and power delivery, while dramatically improving speed and functionality. Here’s a full breakdown of its technical details and core features: Physical structure design 1. USB-C interface features ◦ Reversible plugging:

Understanding the differences in PCB layout between the USB-C 24-pin full-featured and 16-pin USB 2.0 connectors is crucial for ensuring stable device performance. The main distinction lies in the support for high-speed signal lanes, which directly impacts the complexity of layout and routing. The following table compares their key design points. Design Consideration USB-C 24-Pin (Full-Featured) USB-C 16-Pin (USB 2.0
Are you looking for a reliable electronic connector manufacturer to support your business with high-quality products at competitive pricing?
