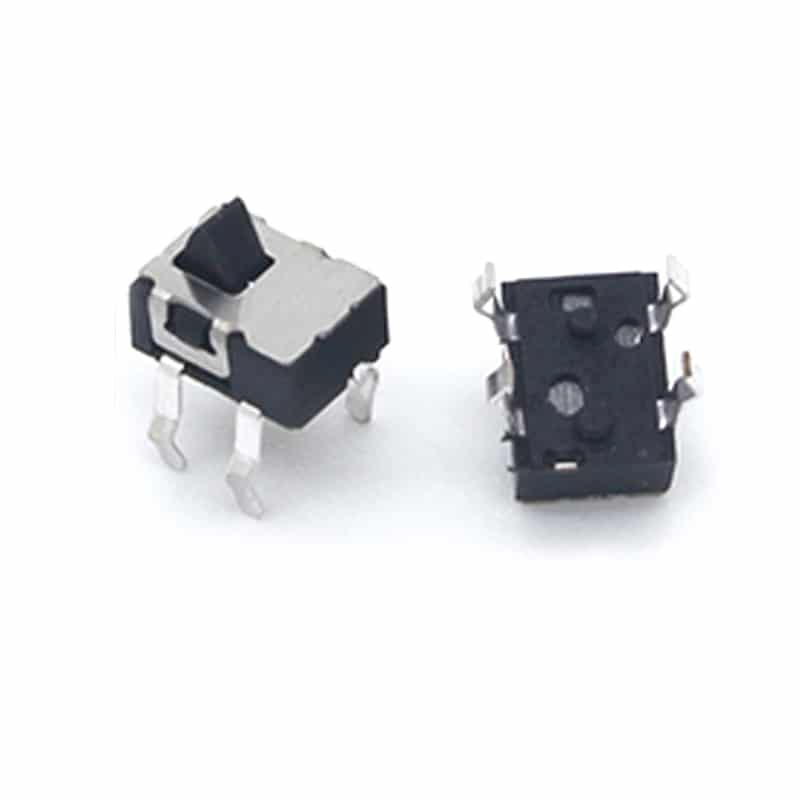
Detect switches, also known as limit switches and sensor switches, are commonly used low-current master control electrical devices.
I. Working Principle
The working principle of a detect switch is based on the opening and closing of circuits. When the switch is in the closed state, current can pass through smoothly, and the circuit is in a conductive state. When the switch is in the open state, current cannot pass through, and the circuit is in a disconnected state.
The detect switch senses changes in parameters within the circuit, such as current, voltage, and temperature, through its internal sensing device. It then compares these sensed parameters with preset thresholds and makes judgments accordingly.
Based on the judgment result, the detect switch outputs corresponding control signals, thereby achieving monitoring and control of the circuit
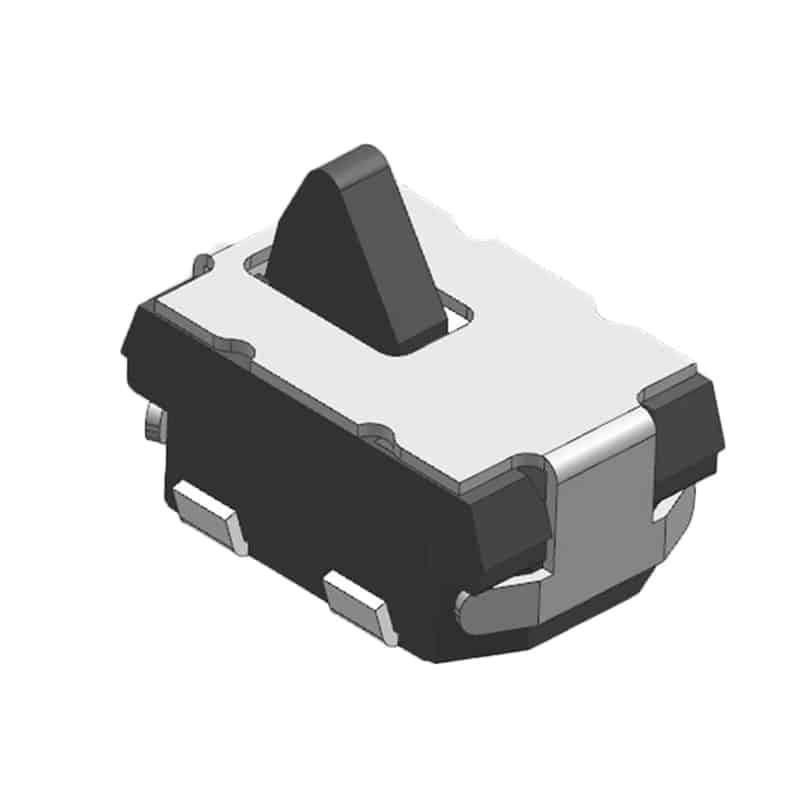

II. Structure of Detect Switches
Detect switches come in various types and have different structures. Common detect switches consist of multiple components, including plug-in components, operating levers, switches, and operating mechanisms.
Some detect switches use various inductive or proximity switches as their main body, which require an external power source to operate.
They typically use micro switches, limit switches, or relay contacts as output switching elements. When connected to electromagnetic switches, small motors, or solenoids, they can handle switching currents of several amperes. several amperes.
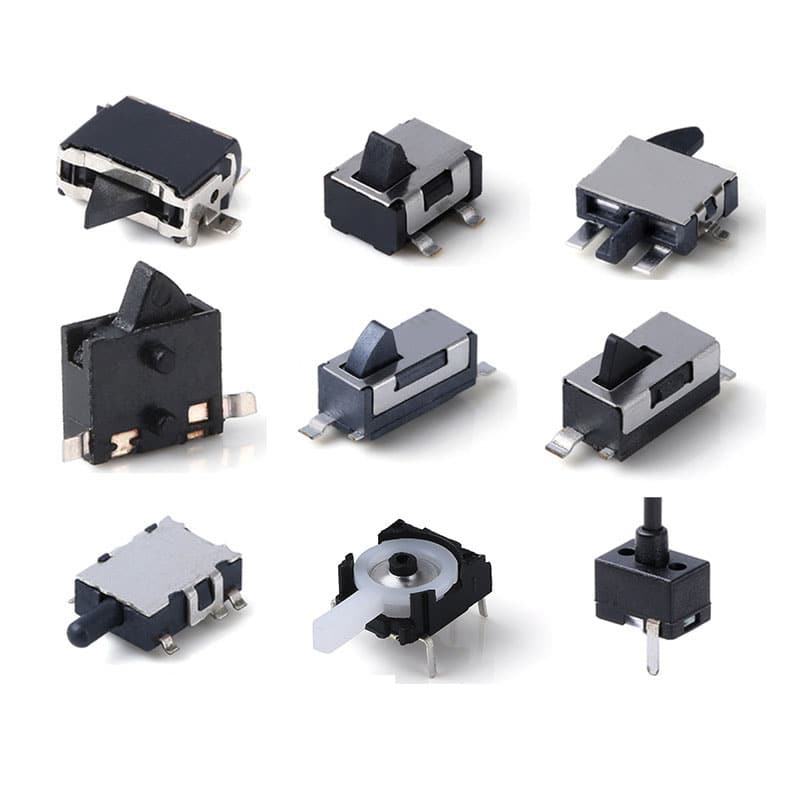
The Type of Detect Switch
Detect switches are available in multiple forms, each designed to respond to specific environmental stimuli or conditions. Common types include:
Motion Detect Switch
This switch is operated by a built-in motion sensor detects movement. It is frequently employed to activate lighting, security alarms, or other electronic devices upon sensing motion, and will turn them off after a predetermined interval with no detected activity.
Photoelectric Switch
Sometimes referred to as an optical sensor switch, this device reacts to variations in light intensity. It can be used to turn on outdoor lights when it gets dark and turn them off when it’s bright enough.
Proximity Switch
Activation of this switch depends on whether an object is present within a defined range. It sees broad usage in industrial settings—for instance, in managing automated equipment or material transport systems.
Temperature Switch
This type triggers when temperature reaches a pre-set value. It is often incorporated into climate control systems such as HVAC units, as well as in industrial operations where precise thermal regulation is necessary.
Pressure Switch
Designed to respond to fluctuations in pressure or vacuum conditions, this switch is commonly installed in pneumatic or hydraulic systems. It also serves in settings that require continuous pressure supervision and adjustment.
Vibration Switch
It can identify oscillations or movements exceeding a specified intensity, this switch is applied in contexts such as equipment condition monitoring or intrusion detector systems.

IV. Application Scenarios
1. Industrial Automation: In equipment such as robots and production lines, detect switches enable the monitoring and control of parameters like component position, distance, speed, and direction, thereby facilitating automated production and industrial intelligence.
2. Security Monitoring: Sensor switches can work in conjunction with sensors for doors, windows, smoke, and fire alarms to perceive and control changes in indoor and outdoor environments, enhancing safety protection measures.
3. Elevator and Railway Systems: In elevators, sensor switches are used to control the speed of door opening and closing, limit automatic door operations, and provide upper and lower limit protection for elevator cars. In railway systems, they are used to monitor train operating status and other information.
4. Power Systems: Sensor switches can be used to monitor circuit current levels, ensuring normal circuit operation.
5. Household Appliances: It can monitor the operating status of appliances, preventing malfunctions that could lead to safety issues.
V. Features and Advantages
1. Real-Time Performance: Sensor switches can promptly sense parameter changes in the circuit and assess the circuit’s operating status in real time.
2. Automated Control: By outputting control signals, sensor switches enable automated control of circuits, reducing the burden of manual operation.
3. Fault Protection: Sensor switches can promptly detect faults in the circuit and take appropriate measures for protection, preventing circuit damage.
4. High Precision and Durability: Due to the short duration of arcing, the contacts suffer minimal damage, giving detector switches high durability and precision.

VI. Selection and Considerations
1. Operating Environment: Choose a detect switch suitable for the temperature, humidity, vibration, and other conditions of the usage environment.
2. Circuit Parameters: Understand the current, voltage, and other parameter ranges of the circuit and select a detect switch that matches them.
3. Precision and Reliability: Choose a detect switch with appropriate precision and reliability based on application requirements.
4. Installation Method: Select the appropriate type of detect switch, such as vertical, horizontal, or embedded, based on the device’s installation space and method.
At the same time, when using detect switches, the following points should be noted:
1. Correct Wiring: Ensure the detect switch is wired correctly to avoid circuit malfunctions or damage due to incorrect connections.
2. Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect and maintain detect switches to ensure normal operation and extend their service life.
3. Avoid Overloading: Prevent detect switches from operating under overload conditions for extended periods to avoid damaging internal components.