01 Background and Release
Not long ago, VESA announced the introduction of the DisplayPort 2.0 (DP 2.0) specification, a milestone event marking an unprecedented leap forward for the DP standard.
Compared to the previous DisplayPort 1.4, the new standard offers a staggering increase in bandwidth capability—up to three times that of its predecessor.
Some might question the need, as DP 1.4 is sufficient for 4K displays. However, with the emergence of Apple’s new 6K Pro Display XDR and the increasing number of 8K displays entering the market, demand for higher bandwidth has arisen. This is precisely the opportunity that DisplayPort 2.0 is designed to address.
▲ VESA and the DP Standard
DisplayPort (DP) is a digital video interface technology developed with the assistance of VESA, offering the advantages of being royalty-free and certification-free.
It was jointly developed by major players in the PC and chip manufacturing industry and standardized by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA).
It has become a preferred interface for connecting video sources to devices like displays, while also supporting the transmission of audio, USB, and other data forms.

▲ The Significance of DP 2.0
With the advent of high-resolution displays, DisplayPort 2.0 provides the necessary higher bandwidth to support 8K and other advanced high-resolution formats.
VESA, the Video Electronics Standards Association, is an international organization focused on setting standards for video devices in computers and small workstations.
The introduction of DisplayPort 2.0 addresses the growing need for bandwidth, enabling 8K and higher-tier resolutions through new technological support and driving progress in video display technology.
02 The Evolution of the DP Standard
Since DP 1.0, VESA has continuously iterated and updated the standard. The DP 1.0 standard, born in May 2006, offered a bandwidth of 10.8 Gbps, a maximum transmission rate of 8.64 Gbit/s, and was limited to a transmission distance of 2 meters.
However, with ongoing technological advancements, this initial standard has become obsolete.
▲ From DP 1.0 to DP 2.0
Subsequently, VESA consistently released new versions of DisplayPort, including 1.1a, 1.2, 1.2a, 1.3, and 1.4, leading up to the current DP 2.0.
The release of DP 2.0 signifies a substantial leap in bandwidth capability, heralding a new era for DisplayPort technology.
03 Technical Features and Advantages
▲ Bandwidth and Resolution Support
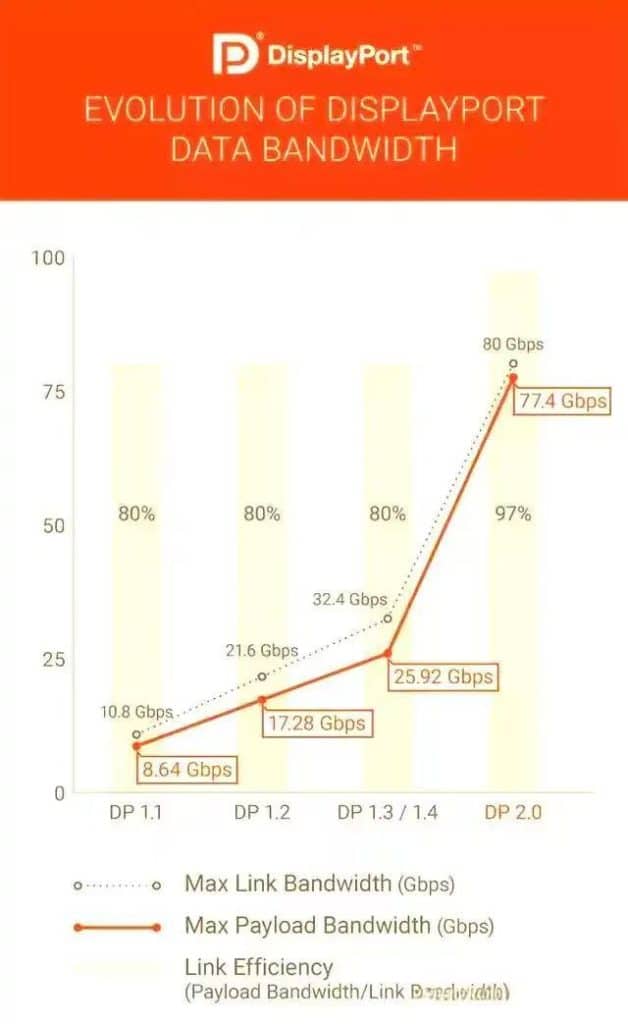
The bandwidth leap of DP 2.0 is particularly noteworthy. DisplayPort 2.0 provides up to 80 Gbps of raw bandwidth, designed to support 8K and beyond for high-resolution displays.
Its fastest mode delivers a remarkable 80 Gbps raw bandwidth, which is approximately 2.5 times that of DisplayPort 1.3/1.4 versions. This significant increase gives DP 2.0 a distinct advantage in bandwidth capacity.
Building on this, DisplayPort 2.0 not only boasts vastly increased bandwidth but also utilizes a more efficient encoding scheme. This allows the new standard to achieve a peak effective bandwidth of up to 77.4 Gbps, representing a nearly threefold increase (2.98x) compared to the previous standard.
With such powerful bandwidth, DisplayPort 2.0 can effortlessly support 8K displays, even with 30-bit color and HDR enabled. Furthermore, it supports 10K displays with uncompressed output at 24-bit color depth.
▲ Connectivity and Data Transmission
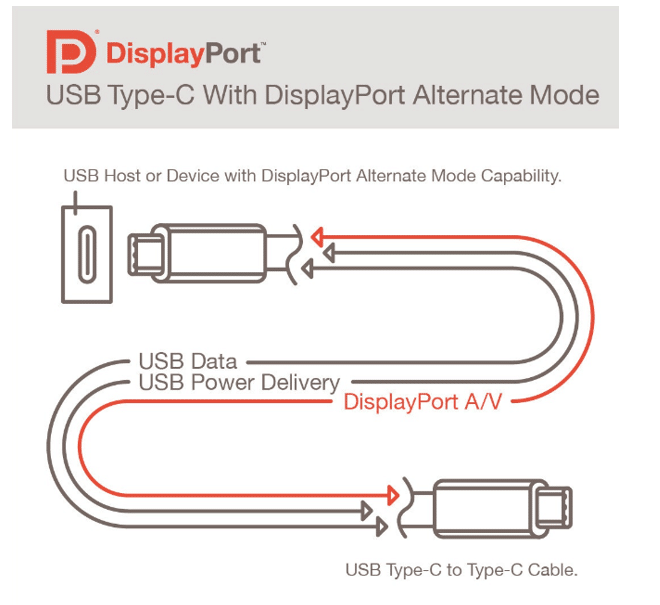
Through the DisplayPort Alt Mode, DP 2.0, combined with Thunderbolt interfaces, provides highly efficient connectivity and enables simultaneous transmission of video and data.
Both native DP connectors and USB Type-C connectors benefit significantly from DP 2.0 technology. Utilizing the USB-C connector, DP 2.0 enhances video bandwidth performance while simultaneously enabling high-speed USB data transfer, all without compromising display performance.
This is facilitated by the integration of the Thunderbolt 3 physical layer, which not only enhances data bandwidth but also promotes the convergence of leading industry I/O standards.
▲ Video Broadcasting and Domestic Breakthroughs
With the launch of 8K TVs and displays, China has made breakthroughs in the 5G transmission of 8K ultra-high-definition content, paving the way for development within the global broadcast industry.
For instance, the video broadcast industry is advancing towards 4K and even 8K resolutions.
Japanese broadcaster NHK announced plans for 8K broadcast of the 2020 Summer Olympics, while China Central Television (CCTV) successfully achieved the country’s first 5G remote transmission of 8K UHD content at the end of June, marking a significant technological breakthrough for China in the field of 8K.